In this article I will discuss about import and export wizard tool. Import and export wizard is the easiest tool to import data or export data from sources to destinations. Sources and destinations can be either SQL server, DB2, Oracle, Excel, flat files or access database.
Import and export wizard uses SSIS framework internally and provides a wizard to import or export data. The complete process done by the wizard can also be saved as an SSIS package.
Import and export wizard can be opened in the below mentioned ways.
- Click on start button select import and export wizard under SQL server installation program
- In SQL server management studio, Right click on database and select import data or export data under tasks options based up on the type which you are doing
- Another option is to open wizard is right click on SSIS folder in BIDS/SSDT environment and selecting import and export wizard.
- You can also open the same wizard by providing command dtswizard.exe on the command prompt or run prompt.
You can choose any of the options to open import and export wizard. Wizard opens with welcome screen as pasted in Figure 1. Irrespective of the operation(import or export) you are performing, the welcome screen is same which explains what can be done using this tool.
Click on next button which opens Source wizard screen where you need to provide source information such as source type and required data base or files. Source connection is the one from which data will be exported.
Options on the data source wizard will be changed based up on the type of data source selected.
Figure 2 shows the options displayed when SQL Native client 10.0 selected as Data source. When SQL native client data source selected, you need to provide server name, authentication type and data base to fetch data
Figure 3 shows the options displayed when Microsoft Excel selected as Data source. Excel file location should provided to export data.
Figure 4 shows options displayed when Flat file source selected as Data Source. You need to provide file location and delimiters when Flat file selected as Data source.
In the same way, you need to provide all required fields based up on the data source selected.
Example: For the purpose of example (copying data from SQL server data base table into flat file), SQL server native client 10.0 selected and all other options provided as shown Figure 5.
Click next button after providing source and required options. Destination wizard will be displayed as shown in Figure 6.
In Destination wizard, you need to provide destination data source and required options. All the data sources which are available in source wizard are available in destination wizard as well.
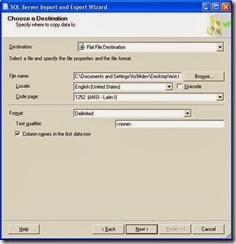
For the purpose of the example, Flat file destination is selected and required options such as file name and delimiters should be selected as shown in Figure 6.
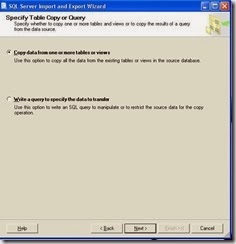
Click next button This option opens another screen where you need to select source tables or views/write a query that you want to transfer to the destination as shown in figure 7. For this example Copy data from one or more table or views options selected and click next button.
When next button clicked, which opens Destination configuration wizard as shown in figure 8 where table or view and delimiters should be specified. If you want you can click on edit mapping options and change default options. Click on Preview to view how data will be stored in flat file. Click next button after completion Destination configuration.
If no errors found, It will take you to save and run package screen. Here you can specify whether you want to execute package immediately or save package either on SQL server or File system for later use.You can also specify how you wish to protect sensitive data in package.
For the purpose of this example i have selected Run immediately and Save SSIS package option(on SQL server) and click next button. You are then taken to save SSIS package screen as shown in Figure 10.
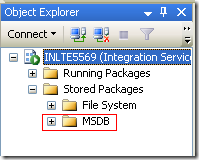
Here you can specify name, description, server name and authentication type to save package. All SSIS Packages will be saved in MSDB database.
Click on next button which takes us to complete the wizard screen as shown in Figure 11 which displays complete details.
After verifying details on complete wizard screen click Finish button this takes you to last screen of the wizard which displays execution of the package as shown in Figure 12
After Executing, data from the table is saved into flat file and Complete process saved as an SSIS package under MSDB database as shown in Figure 13.